| Visitors Now: | |
| Total Visits: | |
| Total Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
NASA Study Shows Health, Food Security Benefits From Climate Change Actions
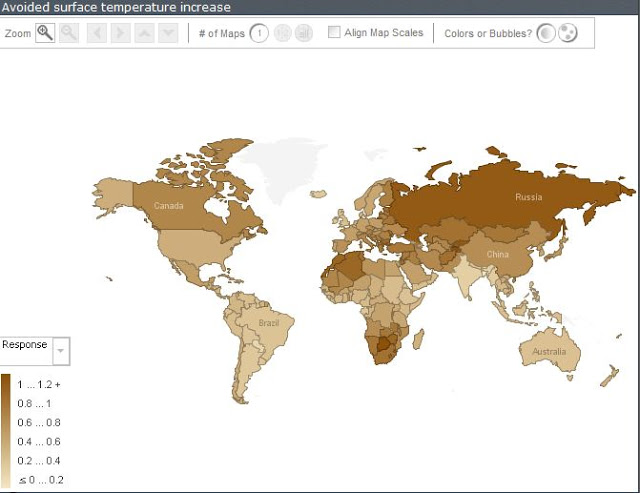
The research, led by Drew Shindell of NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York City, finds that focusing on these measures could slow mean global warming 0.9 ºF (0.5ºC) by 2050, increase global crop yields by up to 135 million metric tons per season and prevent hundreds of thousands of premature deaths each year. While all regions of the world would benefit, countries in Asia and the Middle East would see the biggest health and agricultural gains from emissions reductions.

Shindell and an international team considered about 400 control measures based on technologies evaluated by the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis in Laxenburg, Austria. The new study focused on 14 measures with the greatest climate benefit. All 14 would curb the release of either black carbon or methane, pollutants that exacerbate climate change and human or plant health, either directly or by leading to ozone formation.
While carbon dioxide is the primary driver of global warming over the long term, limiting black carbon and methane are complementary actions that would have a more immediate impact because these two pollutants circulate out of the atmosphere more quickly.
Shindell and his team concluded that these control measures would provide the greatest protection against global warming to Russia, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan, countries with large areas of snow or ice cover. Iran, Pakistan and Jordan would experience the most improvement in agricultural production. Southern Asia and the Sahel region of Africa would see the most beneficial changes to precipitation patterns.
The south Asian countries of India, Bangladesh and Nepal would see the biggest reductions in premature deaths. The study estimates that globally between 700,000 and 4.7 million premature deaths could be prevented each year.
Black carbon and methane have many sources. Reducing emissions would require that societies make multiple infrastructure upgrades. For methane, the key strategies the scientists considered were capturing gas escaping from coal mines and oil and natural gas facilities, as well as reducing leakage from long-distance pipelines, preventing emissions from city landfills, updating wastewater treatment plants, aerating rice paddies more, and limiting emissions from manure on farms.
The scientists used computer models developed at GISS and the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology in Hamburg, Germany, to model the impact of emissions reductions. The models showed widespread benefits from the methane reduction because it is evenly distributed throughout the atmosphere. Black carbon falls out of the atmosphere after a few days so the benefits are stronger in certain regions, especially ones with large amounts of snow and ice.
"Protecting public health and food supplies may take precedence over avoiding climate change in most countries, but knowing that these measures also mitigate climate change may help motivate policies to put them into practice," Shindell said. The new study builds on a United Nations Environment Program/World Meteorological Organization report, also led by Shindell, published last year.
"The scientific case for fast action on these so-called 'short-lived climate forcers' has been steadily built over more than a decade, and this study provides further focused and compelling analysis of the likely benefits at the national and regional level," said United Nations Environment Program Executive Director Achim Steiner.
Contacts and sources:
Adam Voiland/Rani Gran
Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Related Links:
Interactive and embeddable country-by-country graphs and maps
Study in Science
UNEP/WMO Assessment Report
Summary of UNEP/WMO Assessment Report for Policy Makers
Q & A with Drew Shindell
Read more at Nano Patents and Innovations
Source: