| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |
The Elephants of Ether: Mormons and the Mastodon Problem
The Elephants of Ether: Mormons and the Mastodon Problem
2/27/2015
One of the interesting things about doing “research by blog” is that you can get almost instant, unanticipated contributions of information from anyone who reads what you’ve posted. As a result of this post exploring two examples of the idea that “Mound Builders” and mastodons co-existed, I became aware of the interest that Mormons have taken in mastodons. As soon as I wrote the post, Jason Colavito and Brad Lepper each made me aware of the 1839 story Behemoth: A Legend of the Mound Builders by Cornelius Matthews. Behemoth told the tale of the quest of a pre-Native American race (the “Mound-Builders”) to slay a giant mastodon. From there I was led to mentions of elephants in the Book of Mormon (BOM) through this site.
“And the Lord began again to take the curse from off the land, and the house of Emer did prosper exceedingly under the reign of Emer; and in the space of sixty and two years they had become exceedingly strong, insomuch that they became exceedingly rich—Having all manner of fruit, and of grain, and of silks, and of fine linen, and of gold, and of silver, and of precious things; And also all manner of cattle, of oxen, and cows, and of sheep, and of swine, and of goats, and also many other kinds of animals which were useful for the food of man. And they also had horses, and asses, and there were elephants and cureloms and cumoms; all of which were useful unto man, and more especially the elephants and cureloms and cumoms.”
The clear statement about the existence of elephants in the New World at 2500 BC is one of many details in the BOM that critics have questioned and Mormons have defended. As data and scholarly opinions have changed, the Mormon argument has also changed. In the mid 1800s, the idea that mastodons had co-existed with the “Mound Builders” in eastern North America was not uncommon. Currently, however, you would be hard-pressed to find a single non-Mormon scholar who thinks that mastodons survived until anywhere near 2500 BC (a more reasonable estimate would be about 9500 BC). As an archaeologist who works in the Eastern Woodlands, I can tell you that I am not aware of any serious, recent scholarly work that tries to understand the role of mastodons in middle or late Holocene (i.e., post-8000 BC) Native American cultures. Why? Because there is no good evidence that they existed that late into prehistory.
That change in scientific opinion about the timing of mastodon extinction was the result of accumulated paleontological and archaeological knowledge and the development of radiometric dating techniques that allow chronology to be understood in absolute terms (i.e., in terms of real calendar dates). The current Mormon argument for elephants at 2500 BC hinges on just a handful of anomalously late mastodon radiocarbon dates that were obtained in the early decades of radiocarbon dating, before the effects of sample contamination were understood and before procedures were developed to mitigate those effects. By continuing to rely on those dates, Mormon apologists and scholars are clinging to 60-year-old “facts” that they must know are probably in error.
I will discuss the radiocarbon dates further below. But first let’s put the story of mastodons, Mormons, and “Mound Builders” in America in some historical context. Why? Because it’s interesting!
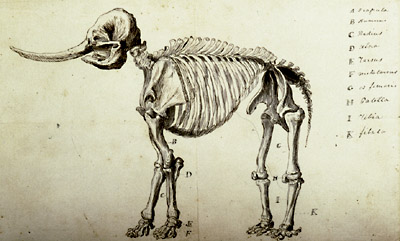 Illustration of the Peale mastodon.
Illustration of the Peale mastodon.
The idea that species could go extinct was still relatively new in the late 1700s. (The absence of the idea of extinction was an important component of why the bones of extinct animals had so often been interpreted as the remains of ancient giants – what else could they be?). The idea of extinction was apparently not one that Thomas Jefferson subscribed to. Consequently, he was convinced that mammoths and mastodons should still be alive in the western part of the continent. In Notes of the State of Virginia (1785:55), Jefferson wrote:
“The bones of the mammoth, which have been found in America, are as large as those found in the old world. It may be asked, why I insert the mammoth, as if it still existed? I ask in return why I should omit it, as if it did not exist? Such is the economy of Nature, that no instance can be produced of her having permitted any one race of her animals to become extinct; of her having formed any link in her great work so weak as to be broken. To add to this, the traditionary testimony of the Indians, that this animal still exists in the Northern and Western parts of America, would be adding the light of a taper to that of the meridian sun. Those parts still remain in their aboriginal state, unexplored and undisturbed by us, or by others for us. He may as well exist there now, as he did formerly, where we find his bones.”
Notice also Jefferson’s plea for recognition of the vigor and size of the North American fauna, of which the mammoth and mastodon were a part. He fully expected that living examples could be found and add to the argument for the grandeur of a young nation. As President of the United States, Jefferson instructed Lewis and Clark to look for mastodons and mammoths during their Corps of Discovery Expedition (1804-1806). After they found none, he ordered excavations at the productive fossil site of Big Bone Lick in Kentucky in 1807 (see A Discourse on the Character and Services of Thomas Jefferson by Samuel Latham Mitchill, 1826, pages 29-30), retrieving mastodon fossils to send to Europe.
More than just a scientific curiosity, mastodons and mammoths were participants in American culture in the early 1800s. The earliest use of the term “mastodon” that I located in a newspaper dates to 1810. Several mastodons were unearthed in New York in the 1810s and 1820s, and those finds were reported in newspapers. The data below show a rapid increase in the appearance of “mastodon” in books (many of them scientific/technical) in the 1820s. Newspapers from this time period also contain numerous advertisements for living elephants exhibited by traveling circuses. My point is that knowledge of both living elephants and their extinct relatives was being widely disseminated when the BOM was published in 1830. Extinct elephants were becoming part of an emerging American identity.
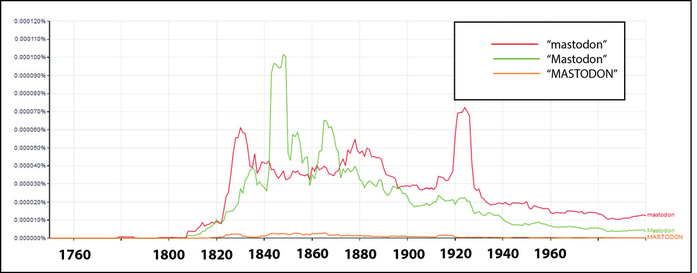
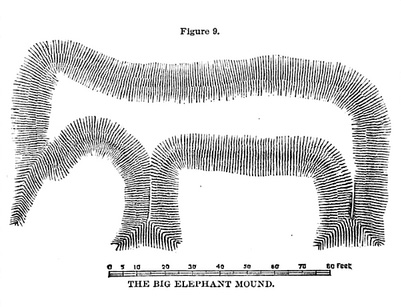 Illustration of the Wisconsin “Elephant Mound” from MacLean’s “Mastodon, Mammoth, and Man” (1880).
Illustration of the Wisconsin “Elephant Mound” from MacLean’s “Mastodon, Mammoth, and Man” (1880).
In the same year as MacLean’s book, Frederick Larkin’s Ancient Man in America was published, describing his theory that the “Mound Builders” had domesticated the mastodon as a beast of burden and for warfare. Larkin also used the elephant-shaped effigy mound in Wisconsin as evidence. A few years later (1885), Charles Putnam published his volume on the elephant pipes of Iowa, widely thought to be fraudulent.
Mormons embraced the array of evidence in the late 1800s that seemed to support the contemporaneity of humans and mastodons in the New World. The 1908 Book of Mormon Talks, written by Hyrum O. Smith, addresses the 1857 critique of Mormonism offered by John Hyde’s Mormonism: Its Leaders and Designs:
“Papa.–We certainly can not blamed for considering this as conclusive evidence in favor of the Book of Mormon account, and rejecting the dogmatic statement of Mr. Hyde that “the elephant is not a native of America and never was its inhabitant.” We have not only found that the elephant was here, but that other large animals of the elephant or mastodon species were here, and that they were here at the same time that man was. These larger animals that are called “cureloms and cumoms” in the Book of Mormon were evidently of the mastodon or elephant type for which there were not names in English, hence their names were transferred to the book just as the Jaredites called them. There is one more point which we wish to establish before we leave this subject. You will notice that the last part of the quotation which Harry has read from Ether says, “And there were elephants, and cureloms, and cumoms; all of which were useful unto man, and more especially the elephants, and cureloms and cumoms.” This certainly signifies that they used these large animals for beasts of burden, and strange to say, we have something to sustain this statement also. Ethel, you may read from page 75 of the Archaeological Committee’s report the opinion of Mr. Frederick Larkin, M.D.:” (pages 141-142)
In the book, Ethel goes on to read Larkin’s self-proclaimed “visionary” statement about the domestication of the mastodon by the “Mound Builders.” Papa gladly accepts Larkin’s conclusion, but chides him for claiming something as “new” which of course had been revealed in an inspired way decades earlier in the BOM.
In the early 1900s, then, the defense of the elephants of Ether was based on a constellation of data points (Central American engravings, apparent associations of mastodons with human tools, fraudulent pipes, an amorphous earthen mound that looks like an elephant if you squint) that suggested the contemporaneity between elephants and the complex societies of the Americas. Larkin’s statement about the domestication of the mastodon was welcomed because the language of the BOM “certainly signifies that they used these large animals for beasts of burden.”
Investigations at the Folsom site in the 1920s cemented the case for all interested parties that humans and extinct Pleistocene animals had co-existed in North America. Excavations at Blackwater Draw in the early 1930s conclusively demonstrated an association between mammoth bones and distinctive Clovis projectile points. The debate about the co-existence of humans and extinct proboscideans was over.
The advent of radiocarbon dating in the early 1950s changed the game of understanding time in prehistoric North America, allowing the ages of organic remains to be estimated in absolute terms (i.e., in calendar years). Almost immediately, the archaeological chronology of North America lengthened significantly as archaeologists were able, for the first time, to understand how much time was really represented by the remains they could observe. Paleontology benefited also, as many fossil remains could be directly dated.
Radiocarbon dates initially seemed to provide support for the idea that mastodons had survived late into prehistory, consistent with the statement in the Book of Ether. As Mormon publications and websites are fond of pointing out, radiocarbon age estimates from mastodons include several mid-Holocene dates that suggest mastodons and the Jaredites could have overlapped. A 2012 paper by John Sorenson in Interpreter: A Journal of Mormon Scripture (volume 1, page 99) reads:
“Mastodon remains have been dated by radiocarbon to around 5000 BC in Florida, around the Great Lakes to 4000 BC, in the Mississippi Valley to near 3300 BC, perhaps to near 100 BC near St. Petersburg, Florida (“low terminal [C-14] dates for the mastodon indicate . . . lingering survival in isolated areas”), and at sites in Alaska and Utah dating around 5000 BC. In the Book of Mormon, mention of elephants occurs in a single verse, in the Jaredite account (“There were elephants,” Ether 9:19), dated in the third millennium BC, after which the record is silent (indicating spot extinction?).”
The website “Step by Step Through the Book of Mormon” repeats some of those dates, as does this website.
As someone who works on Paleoindian period archaeology in eastern North America, I was surprised to see the suggestion that radiocarbon dates indicated the survival of the mastodon into the mid-Holocene. The youngest radiocarbon dates for mastodon of which I was aware are around 10,000-9500 BC (see Woodman and Athfeld 2009). And I’ve never heard of a single mastodon bone being recovered from a context that suggested any interaction with Archaic peoples.
Fortunately, Sorenson’s paper provides some references so we can have a look at these purportedly late dates. Here are the radiocarbon dates I could find that apparently form the basis of the Mormon claim of a late survival of mastodons in eastern North America:
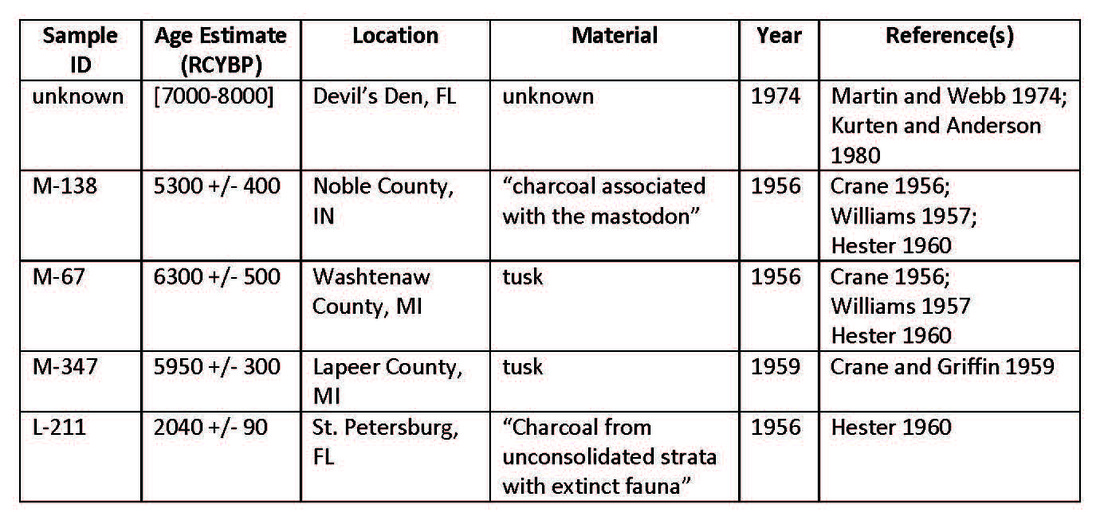
I was also unable to find a specific date associated with the mastodon from Devil’s Den, Florida, and couldn’t find a copy of Martin and Webb (1974) online. Kurten and Anderson (1980:365) reference “unpublished C-14 data” from Martin and Webb (1974) and give an age range of 8000-7000 BP (i.e., about 5000 BC, uncalibrated).
For the other dates, a few things are worth noting. The M-138 date (the “Richmond Mastodon” from Noble County, Indiana) is from charcoal, not the mastodon itself. The association between the charcoal and the mastodon is highly suspect, as the excavation that produced both the mastodon and the charcoal was actually performed in the 1930s (see Williams 1957:365, 368). The excavators thought that the charcoal and some corner-notched projectile points were associated with the mastodon, but it seems more likely they they are actually from a later Late Archaic component that was not directly associated with the mastodon remains. Williams (1957: 368) states that there was a second radiocarbon date from the site that was about twice as old.
The M-67 and M-347 dates, obtained in the 1950s from tusk material, could easily have been contaminated by more recent organic matter (see below). They are most likely far too young.
The L-211 date, like the M-138 date, was apparently obtained from charcoal recovered from an excavation decades earlier. Further, the deposits were unconsolidated and may have contained a jumble of redeposited material (in other words, the charcoal may have had nothing to do with the mastodon bones) (Hester 1960:65).
The alert reader will notice that four out of the five dates in the table above are in the very early years of radiocabon dating (the 1950s), and the fifth is from the 1970s. Why does that matter? Because, as in all science, there have been developments in the methods, practice, and theory of radiocarbon dating since it was first operationalized in 1947. Radiocarbon dating is incredibly important tool for understanding the past, and considerable effort has gone into improving it. One aspect of improving the reliability and accuracy of radiocarbon dating was dealing with problems of sample contamination. Early on, it was realized that radiocarbon dates on bone were often far too young because the samples were often contaminated with more recent carbon.
Here is a summary of the history of advancements in radiocarbon dating bone. Here is another.
The evolution of thought in the scholarly literature about the extinction of mastodons is connected to developments in radiocarbon dating and the refinement of techniques for removing contamination. The 1957 paper by Williams referenced above, often cited by Mormons, argues for the presence of mastodons in eastern North America after 8000 BC, with extinction around 5000 BC. Because of a lack of archaeological associations between mastodon remains and the Archaic peoples with whom they would have been contemporary, however, Williams discussed the possibility of a problem with dating techniques. In other words, the late dates appeared somewhat anomalous even in 1957 because there was no good direct evidence of interactions between mastodons and the Archaic peoples that would have shared the continent with them between 8000 and 5000 BC. All of the radiocarbon dates on bone that Williams utilized would have been subject to contamination by younger carbon, resulting in age estimates that skewed too young.
A 1968 paper by A. Dreimanis summarized 28 available radiocarbon dates for mastodons, throwing out many of the early dates and suggesting that extinction was underway by 10,000 years ago. Dreimanis did not throw out the dates arbitrarily, but because of issues of contamination that were becoming better understood and unclear relationships between what was dated (e.g., plant material) and the target of the date (the mastodon). The paper by Hester (1960) also discusses some of the same problematic dates. By the 1960s, it was recognized that contamination by recent humic acids may make dates on bone collagen too young. Bone samples were especially susceptible to contamination by more recent organic materials, complete removal of which was difficult for the sample sizes that were required.
The advent of accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) dating in the 1980s allowed smaller samples to be used to produce age estimates, permitting improved pretreatment procedures to remove contaminants from bone prior to dating (see this 1992 paper). This improved both the accuracy and precision of radiocarbon dates on bone, which are now typically performed only on collagen (protein) extracted from the bone, rather than the mineral component (hydroxyapatite). Here is an explanation on the Beta Analytic website.
In the present (the early 21st century) all scientists that I’m aware of support the idea that mastodon extinction was associated with the Pleistocene-Holocene transition. The young (e.g., 8000-1000 BC) dates obtained from mastodons in the first decades of radiocarbon dating have not been duplicated (with the possible exception ofvery recent date from another Michigan mastodon) since procedures for removing contaminants were refined. Now a “young” date on a mastodon is one that post-dates 10,500 RCYBP (as above). There are good reasons why scientists don’t use those anomalous dates from the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s: they are not discarded simply because they don’t fit our expectations, but because there are logical, well-understood reasons to strongly suspect they don’t reflect the actual age of the bones. And those dates exist in a vacuum of other compelling evidence to suggest that populations of mastodons really survived that long into the Holocene.
So while radiocarbon dating and science have continued to move forward and refine our understanding of the demise of the mastodons, the Mormons seem to prefer to stop time during the early days of radiocarbon dating, when anomalously young dates on bone were not uncommon. Based on what we know now, those anomalously young dates are probably attributable to either contamination, context/association problems, or both. They are embraced by Mormons not because they are good science, but because they remain the “best fit” to the Jaredite time period. No-one else takes those dates seriously, and it isn’t because they’re trying to undermine the BOM. It’s because there isn’t any reason to take them seriously: they are probably mistakes.
As the scientific evidence against a 2500 BC population of mastodons in eastern North America mounted, the Mormon interpretation of the elephants of Ether also changed. Gone now is any argument that humans had domesticated mastodons, as so confidently asserted by Hyrum O. Smith in 1908. Again from the website “Step by Step Through the Book of Mormon:”
“Moroni then lists the animals that were “useful unto man,” including horses, asses, and the elephants, cureloms, and cumoms. But it is very interesting that there is a difference in the way they are listed. They “had horses and asses,” implying possession of domesticated animals, but “there were elephants, cureloms, and cumoms” (Ether 9:19). This hints that these last mentioned animals existed in the land and were useful to them, but were not domesticated.”
Many Mormon websites also cite as support for the late survival of mastodons evidence of the co-existence of humans and mastodons. Co-existence and late (i.e., 2500 BC) co-existence are not the same thing. The fact that humans and mastodons co-existed has zero bearing on the argument of when they coexisted. There is abundant evidence that humans and mastodons did interact in North America during the Pleistocene-Holocene transition and that fact is not in dispute. What is in dispute in the late survival of those creatures claimed by Mormons. Of that there is no good evidence. Once radiocarbon data allowed prehistoric time in eastern North America to be unfurled, it became clear that there was a large time gap between the heyday of the mastodons the purported arrival of the Jaredites. That time gap grew as radiocarbon dating procedures improved to deal with the systematic error produced by contamination problems.
Continuing to uncritically employ a handful of young radiocarbon dates from the early decades of radiocarbon dating as support for the claim of elephants at 2500 BC is intellectually dishonest. Last time I checked, AMS dates were about $600 each (I also seem to recall that the price has recently dropped). If Mormons want to continue to use radiocarbon dating to evaluate the historical accuracy of the Book of Ether, I suggest that they have those “late surviving” mastodons re-dated. If they agree to pay for it, I would be happy to help attempt to locate the remains wherever they are curated and try to secure permission to have samples dated. It would be a nice way to resolve the ambiguity. We can publish the results. If there really were mastodons tromping around in the woodlands of Archaic eastern North America, I would like to know about it and so would a lot of other people. It’s a win-win.
___________
References for unlinked literature:
Crane, H. R. 1956. University of Michigan Radiocarbon Dates I. Science 124(3224): 664-672.
Crane, H. R., and J. B. Griffin. 1959. University of Michigan Radiocarbon Dates IV. American Journal of Science Radiocarbon Supplement 1: 173-198.
Hester, Jim J. 1960. Late Pleistocene Extinction and Radiocarbon Dating. American Antiquity 26(1):58-77.
Kurten, B., and E. Anderson. 1980. Pleistocene Mammals of North America. New York: Columbia University Press.
Martin, R. A., and S. D. Webb. 1974. Late Pleistocene Mammals from the Devil’s Den Fauna, Levy County. In Webb, S.D. (editor): Pleistocene Mammals of Florida, pp. 114-145. Gainesville: University Presses of Florida.
Williams, Stephen. 1957. The Island 35 Mastodon: Its Bearing on the Age of Archaic Cultures in the East. American Antiquity 22:359-372.




