| Visitors Now: | |
| Total Visits: | |
| Total Stories: |
| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
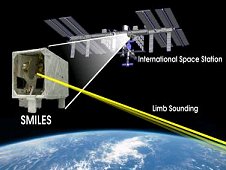
Japan Shares Space Station SMILES via Atmospheric Data Distribution
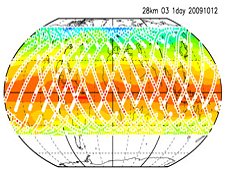 |
| A sample of global distribution of atmospheric minor constituents (ozone) with processing the data in the public release. (JAXA) |
Atmospheric gasses, held in place by gravity, surround our planet and keep us safe from extreme temperatures, ultraviolet radiation, and the vacuum of space. Meanwhile, the magnetic fields generated by and surrounding the Earth — the magnetosphere — help to shield us from the ever-present, solar wind-increased radiation events resulting from CMEs.
The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency, or JAXA, developed a high-precision technology that resides outside the station, mounted on the Japanese Experiment Module–Exposed Facility, or JEM-EF, as part of an investigation to study the chemical makeup of the Earth’s middle atmosphere. Known as the Superconducting Submillimeter-Wave Limb-Emission Sounder, or SMILES, this hardware uses a superconducting detector cooled down to 4K (-269 deg C) and is the first of its kind in space
A cooperation between JAXA and the Japanese National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, or NICT, made the development of SMILES possible. Their combined objective was to use this space station technology to demonstrate highly sensitive submillimeter-wave “the ozone layer.”
The ozone layer helps to protect life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation, and is destroyed by trace atmospheric constituents such as chlorine and bromine that can be produced from human-made refrigerants, solvents, and other compounds. The data collected by SMILES improves our understanding of how these trace atmospheric constituents impact the ozone layer.
A select set of research groups received observation data from SMILES, unique for its high sensitivity detection of atmospheric chemistry. The use of this data can help scientists find answers to questions of climate change, including ozone and global warming research. While SMILES is no longer collecting data, the hardware continues to run as a technology test on orbit.
A recent press release from JAXA announced that the confirmed high-precision data from this study, compiled during a 6 month period ending in April 2010, is now available for release to the public. The SMILES data includes 11 types of atmospheric minor elements, such as chlorine compounds and ozone. This knowledge helps to expand scientific understanding of the atmosphere’s chemical makeup, specifically in the stratosphere and lower mesosphere.
 |
| This video still from March 6, 2012 shows the X5.4 flare captured by the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, in the 171 Angstrom wavelength. (NASA/SDO/AIA) |
Interested scientists can now download this atmospheric chemistry data for study by registering online. They can also e-mail JAXA — including name, affiliation and objectives in less than 50 words — for permission to view the information at [email protected]. Also visit the new International Space Station Benefits for Humanity website for a detailed feature on SMILES.
by Jessica Nimon
International Space Station Program Science Office
NASA’s Johnson Space Center
2012-10-19 05:00:41
Source: http://redonfiles.blogspot.com/2012/03/japan-shares-space-station-smiles-via.html
Source: