| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
Could ‘The Day After Tomorrow’ Happen? Collapse of Atlantic Circulation and Catastrophic Events
In the 2004 film, climate warming caused an abrupt collapse of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC), leading to catastrophic events such as tornadoes destroying Los Angeles, New York being flooded and the nort
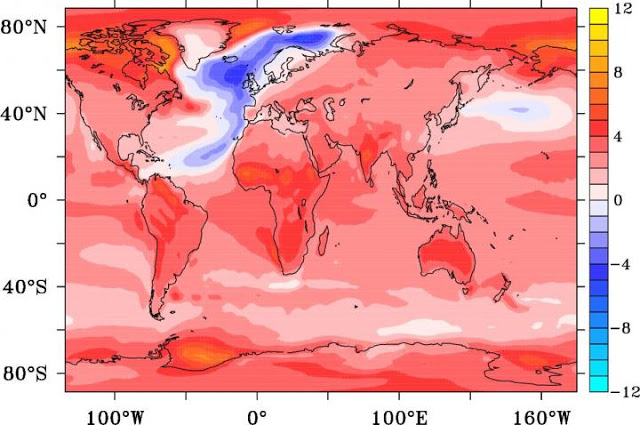
Using the German climate model ECHAM at the Max-Planck Institute in Hamburg, Professor Sybren Drijfhout from Ocean and Earth Science at the University of Southampton found that, for a period of 20 years, the earth will cool instead of warm if global warming and a collapse of the AMOC occur simultaneously. Thereafter, global warming continues as if the AMOC never collapsed, but with a globally averaged temperature offset of about 0.8°C.
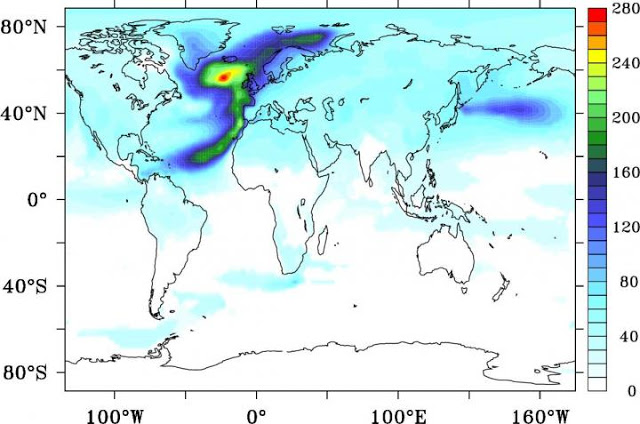
This image shows recovery time in years, defined as the time needed for surface air temperature to recover its values from 1990-2000
Professor Drijfhout said: “The planet earth recovers from the AMOC collapse in about 40 years when global warming continues at present-day rates, but near the eastern boundary of the North Atlantic (including the British Isles) it takes more than a century before temperature is back to normal.”
Interestingly, the effect of atmospheric cooling due to an AMOC collapse is associated with heat flow from the atmosphere into the ocean, which has been witnessed during the climate hiatus of the last 15 years.
Professor Drijfhout added: “When a similar cooling or reduced heating is caused by volcanic eruptions or decreasing greenhouse emissions the heat flow is reversed, from the ocean into the atmosphere. A similar reversal of energy flow is also visible at the top of the atmosphere. These very different fingerprints in energy flow between atmospheric radiative forcing and internal ocean circulation processes make it possible to attribute the cause of a climate hiatus period.”
However, the study, which appears in Scientific Reports, says that the recent period of very weak warming cannot be attributed to one single cause. Most probably El Niño plays a role and possibly also changes in the Southern Ocean due to shifting and increasing westerlies.
Professor Sybren said: “It can be excluded, however, that this hiatus period was solely caused by changes in atmospheric forcing, either due to volcanic eruptions, more aerosols emissions in Asia, or reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Changes in ocean circulation must have played an important role. Natural variations have counteracted the greenhouse effect for a decade or so, but I expect this period is over now.”
Glenn Harris
Source: http://www.ineffableisland.com/2015/10/could-day-after-tomorrow-happen.html