| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
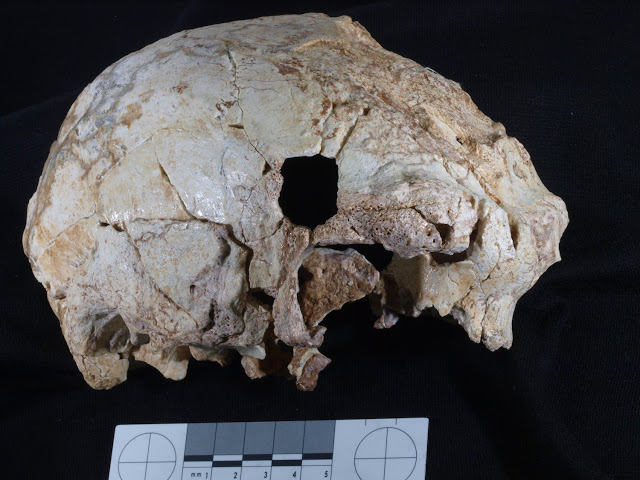
400,000-Year-Old Fossil Human Cranium Is Oldest Ever Found in Portugal Points to Neanderthal Origin
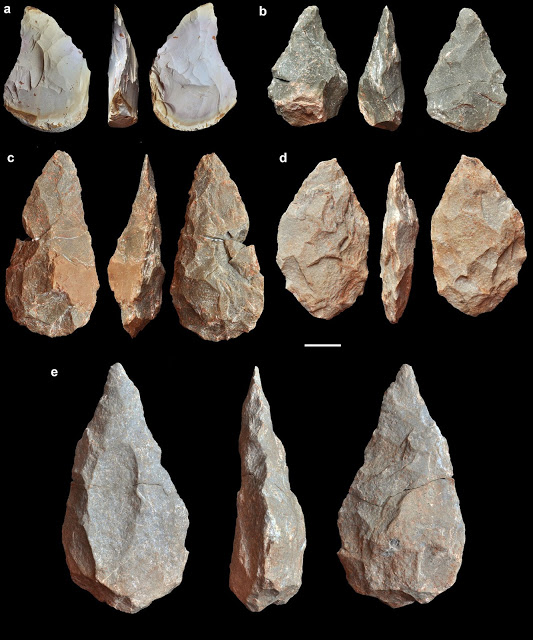
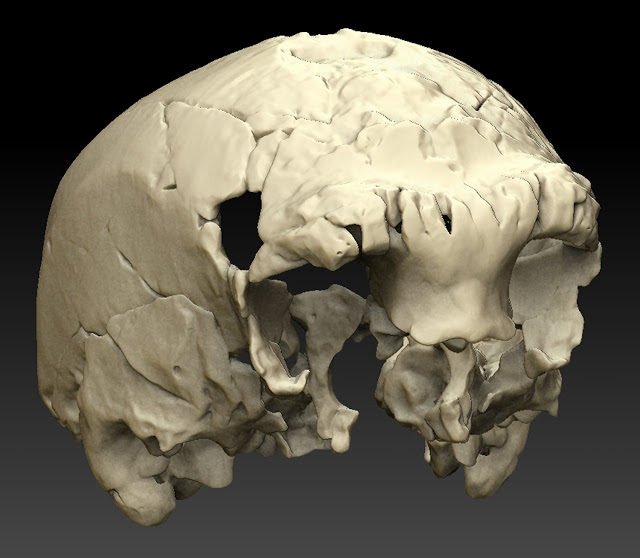
The cranium represents the westernmost human fossil ever found in Europe during the middle Pleistocene epoch and one of the earliest on this continent to be associated with the Acheulean stone tool industry. In contrast to other fossils from this same time period, many of which are poorly dated or lack a clear archaeological context, the cranium discovered in the cave of Aroeira in Portugal is well-dated to 400,000 years ago and appeared in association with abundant faunal remains and stone tools, including numerous bifaces (handaxes).
The cranium was found on the last day of the 2014 field season. Since the sediments containing the cranium at the Aroeira site were firmly cemented, the cranium was removed from the site in a large, solid block. It was then transported to the restoration laboratory at the Centro de Investigacion sobre la Evolucion y Comportamiento Humanos, a paleoanthropology research center in Madrid, Spain, for preparation and extraction, a painstaking process which took two years.
“The results of this study are only possible thanks to the arduous work of numerous individuals over the last several years,” said Quam. “This includes the archaeologists who have excavated at the site for many years, the preparator who removed the fossil from its surrounding breccia, researchers who CT scanned the specimen and made virtual reconstructions and the anthropologists who studied the fossil. This study truly represents an international scientific collaboration, and I feel fortunate to be involved in this research.”
The new fossil will form the centerpiece of an exhibit on human evolution in October at the Museu Nacional de Arqueologia in Lisbon, Portugal.
Source: http://www.ineffableisland.com/2017/03/400000-year-old-fossil-human-cranium-is.html