

| Visitors Now: | |
| Total Visits: | |
| Total Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
Cygnus OB2: Probing A Nearby Stellar Cradle
Cygnus OB2 is a star cluster in the Milky Way that contains many hot, massive young stars.
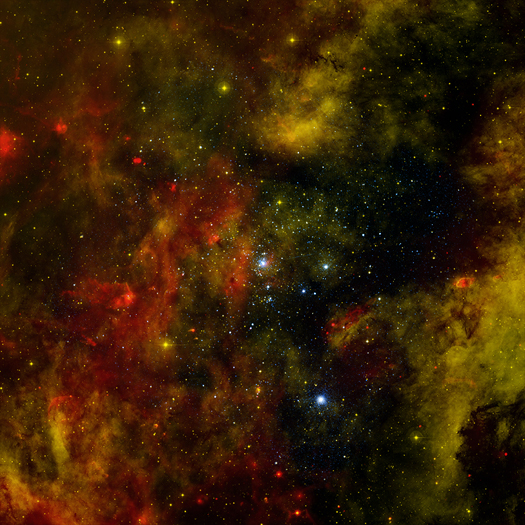

Astronomers would like to better understand how this and other star factories like it form and evolve.
A deep Chandra observation of Cygnus OB2 has found almost 1,500 stars emitting X-rays.
The Milky Way and other galaxies in the universe harbor many young star clusters and associations that each contain hundreds to thousands of hot, massive, young stars known as O and B stars. The star cluster Cygnus OB2 contains more than 60 O-type stars and about a thousand B-type stars. At a relatively nearby distance to Earth of about 5,000 light years, Cygnus OB2 is the closest massive cluster.
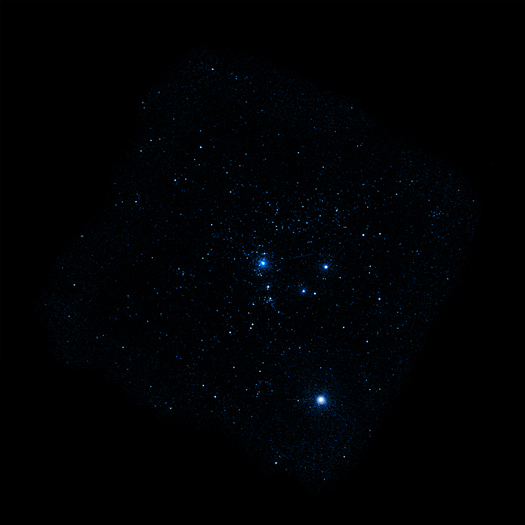

Young stars ranging in age from one million to seven million years were detected. The infrared data indicates that a very low fraction of the stars have circumstellar disks of dust and gas. Even fewer disks were found close to the massive OB stars, betraying the corrosive power of their intense radiation that leads to early destruction of their disks.
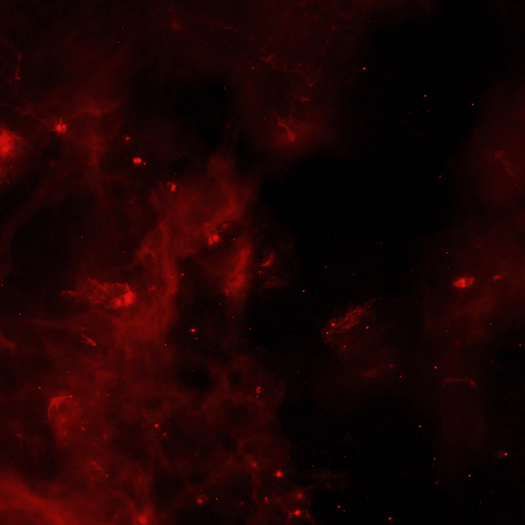
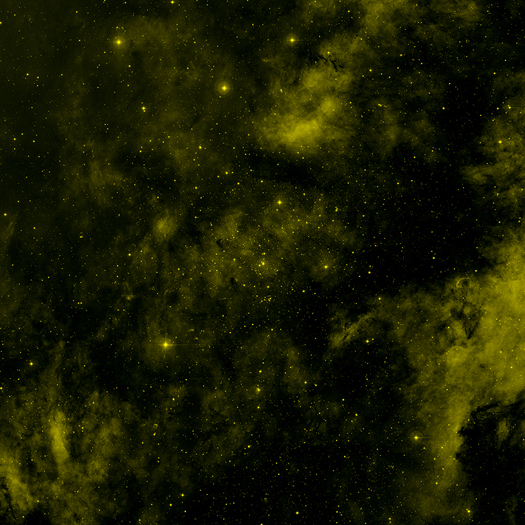
NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., manages the Chandra program for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls Chandra’s science and flight operations from Cambridge, Mass.


