| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
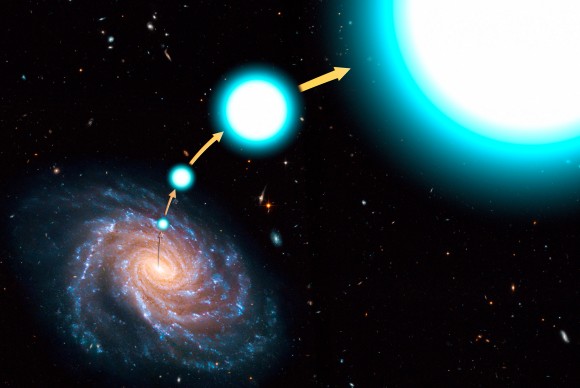
Planets Could Travel Along with Rogue ‘Hypervelocity’ Stars, Spreading Life Throughout the Universe
Back in 1988, astronomer Jack Hills predicted a type of “rogue”star might exist that is not bound to any particular galaxy. These stars, he reasoned, were periodically ejected from their host galaxy by some sort of mechanism to begin traveling through interstellar space.
Since that time, astronomers have made numerous discoveries that indicate these rogue, traveling stars indeed do exist, and far from being an occasional phenomenon, they are actually quite common. What’s more, some of these stars were found to be traveling at extremely high speeds, leading to the designation of hypervelocity stars (HVS).
And now, in a series of papers that published in arXiv Astrophysics, two Harvard researchers have argued that some of these stars may be traveling close to the speed of light. Known as semi-relativistic hypervelocity stars (SHS), these fast-movers are apparently caused by galactic mergers, where the gravitational effect is so strong that it fling stars out of a galaxy entirely. These stars, the researchers say, may have the potential to spread life throughout the Universe.
(…)
Read the rest of Planets Could Travel Along with Rogue ‘Hypervelocity’ Stars, Spreading Life Throughout the Universe (759 words)
© mwill for Universe Today, 2014. |
Permalink |
No comment |
Post tags: galaxy merger, HVS, hypervelocity star, NASA, panspermia, semi-relativistic hypervelocity stars, SHS, SMBH, speed of light, supermassive black hole, Theory of Relativity
Feed enhanced by Better Feed from Ozh
Source: http://www.universetoday.com/116872/planets-could-travel-along-with-rogue-hypervelocity-stars-spreading-life-throughout-the-universe/