| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
Astronomers Find Galaxy 13.1 Billion Light-Years Away… Big Bang Occurred Around 13.8 Billion Years Ago!
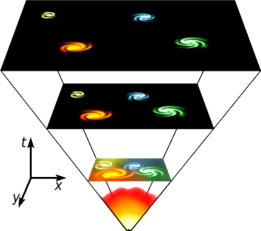
According to the Big Bang model, the universe expanded from an extremely dense and hot state and continues to expand today.
Astronomers have spotted a baby blue galaxy that is farther away in space and time than any other galaxy ever seen. It is among the universe’s first generation of galaxies, from approximately 13.1 billion years ago.
Yale and University of California Santa Cruz scientists used three telescopes to spot and calculate the age of the blurry infant galaxy. By measuring how the light has shifted, they determined the galaxy, named EGS-zs8-1, is from about 670 million years after the Big Bang.
Because when astronomers look farther away from Earth, they are looking back further in time, this is both the most distant galaxy and the furthest back in time. It is 13.1 billion light-years away, in the constellation Bootes. A light-year is 5.8 trillion miles.
This beats the old record by about 30 million years, which isn’t much, but was difficult to achieve, said astronomer Garth Illingworth of the University of California Santa Cruz, who co-authored the paper in Astrophysical Journal Letters announcing the discovery.
The photo they took was from a crucial time in the early universe, after what was called t
he Dark Ages, when galaxies and stars were just starting to form and the universe was only one five hundredth the mass it is now, Illingworth said.
This galaxy – larger than most of the others from that time, which is why astronomers using the most powerful telescopes can see it – was probably only about 100 million years also, but was quite busy, Illingworth said.
logical model for the universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution.[1][2][3] It states that the universe was in a very high density state and then expanded.[4][5] If the known laws of physics are extrapolated beyond where they are valid there is a singularity. Modern measurements place this moment at approximately 13.8 billionyears ago, which is thus considered the age of the universe.[6] After the initial expansion, the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later simple atoms. Giant clouds of these primordial elements later coalesced through gravity to form stars and galaxies.
In the mid-20th century, three British astrophysicists, Stephen Hawking, George Ellis, and Roger Penroseturned their attention to the Theory of Relativity and its implications regarding our notions of time. In 1968 and 1970, they published papers in which they extended Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity to include measurements of time and space.[7][8] According to their calculations, time and space had a finite beginning that corresponded to the origin of matter and energy.
astronomers-find-galaxy-131-billion-light-years away