| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
Most Detailed View Ever of Star Formation in the Distant Universe
ALMA’s Long Baseline Campaign has produced a spectacularly detailed image of a distant galaxy being gravitationally lensed. The image shows a magnified view of the galaxy’s star-forming regions, the likes of which have never been seen before at this level of detail in a galaxy so remote. The new observations are far more detailed than those made using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, and reveal star-forming clumps in the galaxy equivalent to giant versions of the Orion Nebula.
Credit: ALMA (NRAO/ESO/NAOJ)/Luis Calçada (ESO)
The middle image shows the sharp ALMA image of the Einstein ring, with the foreground lensing galaxy being invisible to ALMA. The resulting reconstructed image of the distant galaxy (right) using sophisticated models of the magnifying gravitational lens, reveal fine structures within the ring that have never been seen before: Several dust clouds within the galaxy, which are thought to be giant cold molecular clouds, the birthplaces of stars and planets.
At least seven groups of scientists [3] have independently analysed the ALMA data on SDP.81. This flurry of research papers has divulged unprecedented information about the galaxy, revealing details about its structure, contents, motion, and other physical characteristics.
Credit: ALMA (NRAO/ESO/NAOJ)/Luis Calçada (ESO)
The astronomers’ sophisticated models reveal fine, never-before-seen structure within SDP.81, in the form of dusty clouds thought to be giant repositories of cold molecular gas — the birthplaces of stars and planets. These models were able to correct for the distortion produced by the magnifying gravitational lens.
As a result, the ALMA observations are so sharp that researchers can see clumps of star formation in the galaxy down to a size of about 200 light-years, equivalent to observing giant versions of the Orion Nebula producing thousands of times more new stars at the far side of the Universe. This is the first time this phenomenon has been seen at such an enormous distance.
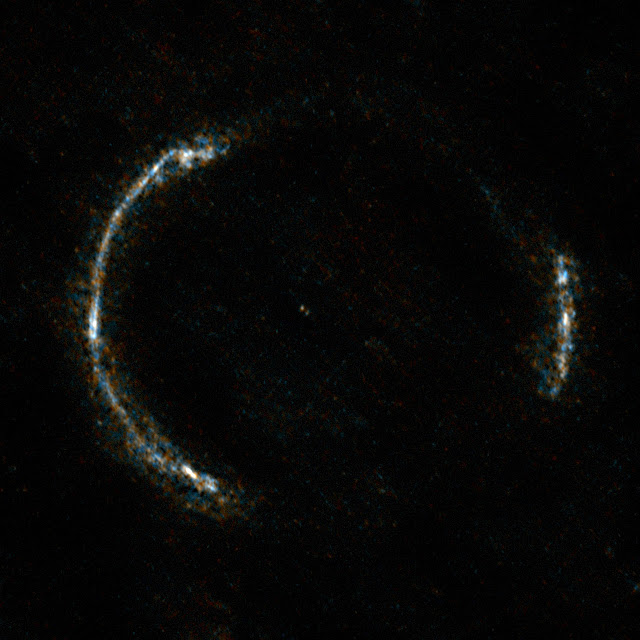

Credit:ALMA (NRAO/ESO/NAOJ)/Y. Tamura (The University of Tokyo)
Using the spectral information gathered by ALMA, astronomers also measured how the distant galaxy rotates, and estimated its mass. The data showed that the gas in this galaxy is unstable; clumps of it are collapsing inwards, and will likely turn into new giant star-forming regions in the future.
Note that some of the smaller structures visible here might be artifacts caused by the reconstruction method.
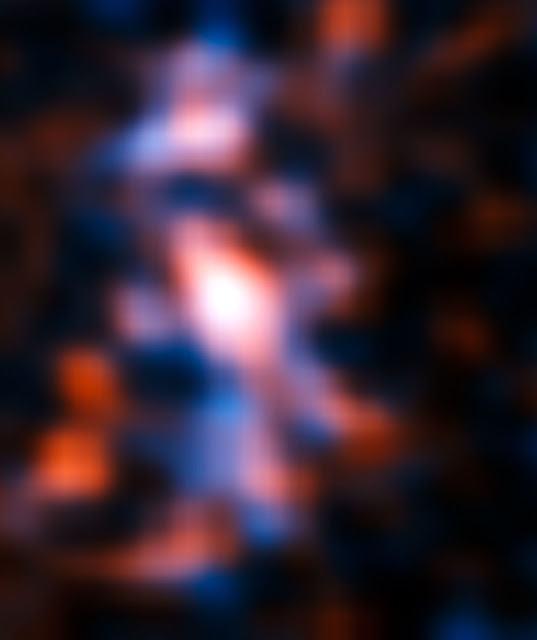
Credit: ALMA (NRAO/ESO/NAOJ)/Mark Swinbank (Durham University)
The number of papers published using this single ALMA dataset demonstrates the excitement generated by the potential of the array’s high resolution and light-gathering power. It also shows how ALMA will enable astronomers to make more discoveries in the years to come, also uncovering yet more questions about the nature of distant galaxies.
Notes
[1] The lensed galaxy is seen at a time when the Universe was only 15 percent of its current age, just 2.4 billion years after Big Bang. The light has taken over twice the age of the Earth to reach us (11.4 billion years), detouring along the way around a massive foreground galaxy that is comparatively close at four billion light-years away from us.
[2] Gravitational lenses were predicted by Albert Einstein as part of his theory of general relativity. His theory tells us that objects bend space and time. Any light approaching this curved space-time will itself follow the curvatures created by the object. This enables particularly massive objects — huge galaxies and galaxy clusters — to act as cosmic magnifying glasses. An Einstein ring is a special type of gravitational lens, in which the Earth, the foreground lensing galaxy, and the background lensed galaxy are in perfect alignment, creating a harmonious distortion in the form of a ring of light. This phenomenon is illustrated in Video A.
[3] The science teams are listed below.
[4] ALMA’s ability to see the finest detail is achieved when the antennas are at their greatest separation, up to 15 kilometres apart. For comparison, earlier observations of gravitational lenses made with ALMA in a more compact configuration, with a separation of only around 500 metres, can be seen here.
[5] Details down to 0.023 arc-seconds, or 23 milli-arcseconds, can be measured in these data. Hubble observed this galaxy in the near-infrared, with a resolution of about 0.16 arc-seconds. Note, however, that when observing at shorter wavelengths, Hubble can reach finer resolutions, down to 0.022 arcseconds in the near-ultraviolet. ALMA’s resolution can be adjusted depending on the type of observations by moving the antennas further apart or closer together. For these observations, the widest separation was used, resulting in the finest resolution possible.
[6] The high-resolution ALMA image enables researchers to look for the central part of the background galaxy, which is expected to appear at the centre of the Einstein ring. If the foreground galaxy has a supermassive black hole at the centre, the central image becomes fainter. The faintness of the central image indicates how massive the black hole in the foreground galaxy is.
Contacts and sources:
Lars Lindberg Christensen
Source:




