| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
Riding ‘Drifting Carousel’ to Understand Pulsars, the ‘Lighthouses in Space’
New research from Curtin University, obtained using the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) radio telescope located in the Western Australian outback, suggests the answer could lie in a ‘drifting carousel’ found in a special class of pulsars.
Curtin PhD student Sam McSweeney, who led the research as part of his PhD project with the ARC Centre of Excellence for All-sky Astrophysics (CAASTRO) and the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR), described pulsars as extremely dense neutron stars that emit beams of radio waves.
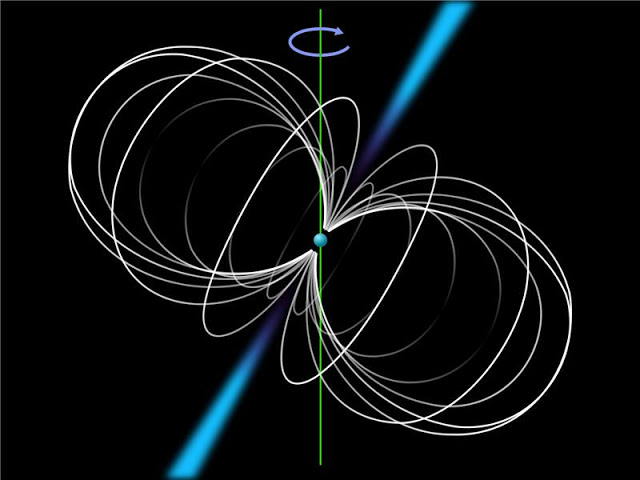
“These pulsars weigh about half a million times the mass of the Earth but are only 20km across,” Mr McSweeney said.Schematic view of a pulsar. The sphere in the middle represents the neutron star, the curves indicate the magnetic field lines and the protruding cones represent the emission zones.
“They are nicknamed ‘lighthouses in space’ because they appear to ‘pulse’ once per rotation period, and their sweeping light signal can be seen through telescopes at exceptionally regular intervals.”
Thousands of pulsars have been seen since their first discovery in the late 1960s, but questions still remain as to why these stars emit radio beams in the first place, and what type of emission model best describes the radio waves, or ‘light’, that we see.
“The classical pulsar model pictures the emission that is shooting out from the magnetic poles of the pulsar as a light cone,” Mr McSweeney said.
“But the signal that we observe with our telescopes suggests a much more complex structure behind this emission – probably coming from several emission regions, not just one.”
“As each patch releases radiation, the rotation generates a small drift in the observed signal of these sub-pulses that we can detect using the MWA,” Mr McSweeney said.
“Occasionally, we find that this sub-pulse carousel gets faster and then slower again, which can be our best window into the plasma physics underlying the pulsar emission.”
One possibility the researchers are currently testing is that surface temperature is responsible for the carousel changing rotation speed: localised ‘hotspots’ on the pulsar surface might cause it to speed up.
“We will observe individual pulses from these drifting pulsars across a wide range of radio frequencies, with lower frequency data than ever before,” Mr McSweeney said.
“Looking at the same pulsar with different telescopes simultaneously will allow us to trace the emission at different heights above their surface.”
The researchers plan to combine the data from the MWA, the Giant Metre-wave Radio Telescope in India and the CSIRO Parkes Radio Telescope in New South Wales to – literally – get to the bottom of the mysterious pulses.
A paper explaining the research “Low Frequency Observations of the Subpulse Drifter PSR J0034-0721 with the Murchison Widefield Array” was recently published in The Astrophysical Journal.
CAASTRO is a collaboration of The University of Sydney, The Australian National University, The University of Melbourne, Swinburne University of Technology, The University of Queensland, The University of Western Australia and Curtin University, the latter two participating together as the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR). CAASTRO is funded under the Australian Research Council (ARC) Centre of Excellence program, with additional funding from the seven participating universities and from the NSW State Government’s Science Leveraging Fund.
ICRAR is a joint venture between Curtin University and The University of Western Australia and supported by the Western Australian Government.
The Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) is a low frequency radio telescope located at the Murchison Radio-astronomy Observatory in Western Australia’s Mid-West. The MWA observes radio waves with frequencies between 70 and 320 MHz and was the first of the three Square Kilometre Array (SKA) precursors to be completed.
Contacts and sources:
Sam McSweeney
CAASTRO, ICRAR, Curtin Institute of Radio Astronomy
Source: