| Visitors Now: | |
| Total Visits: | |
| Total Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
Earth Has A Companion Asteroid With a Weird Orbit … EYE Report

 This asteroid was discovered on September 17, 2010 by the WISE Earth-orbiting observatory.
This asteroid was discovered on September 17, 2010 by the WISE Earth-orbiting observatory.
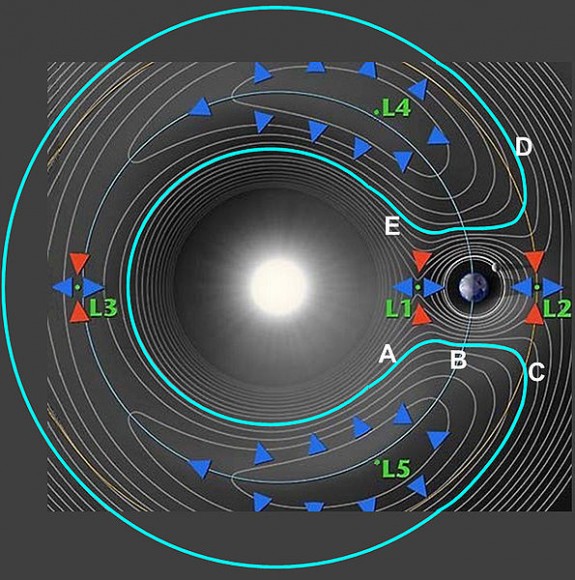
In this graphic of a horseshoe orbit from NASA, Horseshoe orbits follow contour lines that enclose Lagrange points L3, L4 & L5. Credit: NASA
There are plenty of near-Earth asteroids out there, but this latest one studied by two researchers at Armagh Observatory in Northern Ireland is extremely rare in that it has a weird, horseshoe-shaped orbit. Not that Asteroid 2010 SO16 does an about-face and turns around in mid-orbit — no, the asteroid always orbits the Sun in the same direction. But because of its unique orbital path and the gravitational effects from both the Earth and the Sun, it goes through a cycle of catching up with the Earth and falling behind, so that from our perspective here on Earth, its movement relative to both the Sun and the Earth traces a shape like the outline of a horseshoe: it appears to approach, then shift orbit, and go farther away without ever passing Earth.
There are only a handful of other asteroids known to have a horseshoe orbit. But astronomers Apostolos Christou and David Asher say 2010 SO16’s absolute magnitude (H=20.7) makes this the largest object of its type known to-date. It is just a few hundred meters across, so the other asteroids are extremely small, and none of the other horseshoe asteroids have orbits that are likely to survive for more than a few thousand years. But the researchers did computer simulations of SO16’s orbit, which showed it could stay in its orbit for at least 120,000 years, maybe more.
For an asteroid to have such an orbit means it is in almost the same solar orbit as Earth, and both take approximately one year to orbit the Sun.