| Visitors Now: | |
| Total Visits: | |
| Total Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
The Collapse Will Be Much Worse With The Forecasted Drought And Food Storages
Yesterday, August 05, 2012
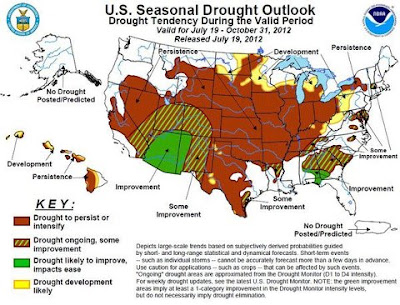
So what's new with a drought? Haven't we always had some sort of drought warning? Aren't we big enough as a country to mitigate drought effects? The answers Drought Forecasted
A double-barreled dose of bad news came out Thursday: Not only did the drought worsen over the last week, but it's likely to widen and intensify through the end of October, according to the seasonal outlook prepared by government forecasters.
"Unfortunately, all indicators (short and medium-term, August, and August-October) favor above normal temperatures," the National Weather Service's Climate Prediction Center said in its Seasonal Drought report."We don't see a reason to say it will improve," Kelly Helm Smith, a specialist at the National Drought Mitigation Center, told reporters. "I'm in the Midwest," she said, referring to her office at the University of Nebraska in Lincoln, "it's really unpleasant."
The outlook noted that "a dramatic shift in the weather pattern" would be required "to provide significant relief to this drought, and most tools and models do not forecast this." Drought could take hold in the northern plains by October, the Climate Prediction Center added Moreover, last week saw a continued "downward spiral of drought conditions," according to the weekly report.
Adding to the drought concerns is Lester R. Brown, author of an article titled: "The world is closer to a food crisis than most people realise". He is the president of the Earth Policy Institute and also the author of Full Planet, Empty Plates: The New Geopolitics of Food Scarcity, due to be published in October
In the early spring this year, US farmers were on their way to planting some 96millon acres in corn, the most in 75 years. A warm early spring got the crop off to a great start. Analysts were predicting the largest corn harvest on record.
The United States is the leading producer and exporter of corn, the world's feedgrain. At home, corn accounts for four-fifths of the US grain harvest. Internationally, the US corn crop exceeds China's rice and wheat harvests combined. Among the big three grains – corn, wheat, and rice – corn is now the leader, with production well above that of wheat and nearly double that of rice.
The corn plant is as sensitive as it is productive. Thirsty and fast-growing, it is vulnerable to both extreme heat and drought. At elevated temperatures, the corn plant, which is normally so productive, goes into thermal shock.
As spring turned into summer, the thermometer began to rise across the corn belt. In St Louis, Missouri, in the southern corn belt, the temperature in late June and early July climbed to 100F or higher 10 days in a row. For the past several weeks, the corn belt has been blanketed with dehydrating heat.
Weekly drought maps published by the University of Nebraska show the drought-stricken area spreading across more and more of the country until, by mid-July, it engulfed virtually the entire corn belt. Soil moisture readings in the corn belt are now among the lowest ever recorded.