

| Visitors Now: | |
| Total Visits: | |
| Total Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
“The Great Dying” The Worst Extinction in Earth’s History
When tectonics killed everything
A new paper reveals how the worst extinction in Earth’s history may have been tied to the formation of Supercontinent Pangea. The catastrophe wasn’t triggered by an impact from above—unlike another well-known extinction—but by a geological process below, deep within Earth’s core.
t’s often known as “The Great Dying.”

Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-11 (GEOS-11) image of the Earth acquired on June 14, 2000. Credit: NOAA
About 252 million years ago, all life nearly vanished. More than 90 percent of ocean species and 70 percent of land species died. Trees, plants, reptiles, fish, insects, microbes—all nearly wiped out.
The event marked the end of the Permian period and the beginning of the Triassic, the period that would give rise to the dinosaurs. But unlike the later Cretaceous extinction, the one that’d kill off the dinosaurs 186 million years later, this one wasn’t caused by an asteroid impact, most scientists think. The ultimate trigger, in fact, has remained an ongoing mystery.
Scientists have unearthed many clues over the last decades, but they’ve yet to reach a final verdict. So far the evidence has pointed toward drastic changes on Earth and in the oceans. Oxygen levels were low in the oceans, making it difficult for many animals to survive.
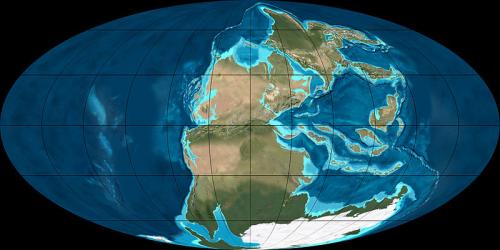
Late Permian (260 million years ago) — All the world’s lands had joined into a single supercontinent, Pangea, and all the world’s sea water had formed a global ocean, Panthalassa. Credit: Ron Blakey, NAU Geology
Carbon dioxide and methane levels were unusually high, contributing to major warming of the planet. Acid rain fell, and made sea water so acidic that all coral reefs disappeared. The inland turned into an dry desert, hot and arid, and devastated by major wild fires. The climate also varied between periods of sudden warming and cooling, making it impossible for many species to adjust.
Journal reference: Science China Earth Sciences
Source: Astrobio.net
PHYS.ORG
Read more here: http://phys.org/news/2013-11-tectonics.html


