| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
TradCatKnight; Mark of the Beast Watch: Employees In Europe Getting Implanted With Microchips
Monday, April 3, 2017 17:24
% of readers think this story is Fact. Add your two cents.
Mark of the Beast Watch: Employees In Europe Getting Implanted With Microchips
Mark of the Beast Watch: Employees In Europe Getting Implanted With Microchips
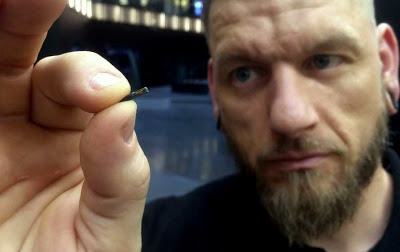
Self-described “body hacker” Jowan Osterlund from Biohax Sweden, holds a small microchip implant, similar to those implanted into workers at the Epicenter digital innovation business centre during a party at the co-working space in central Stockholm, Tuesday March 14, 2017. (Photo: James Brooks/AP)
STOCKHOLM — The syringe slides in between the thumb and index finger. Then, with a click, a microchip is injected in the employee’s hand. Another “cyborg” is created.
What could pass for a dystopian vision of the workplace is almost routine at the Swedish startup hub Epicenter. The company offers to implant its workers and startup members with microchips the size of grains of rice that function as swipe cards: to open doors, operate printers, or buy smoothies with a wave of the hand.
The injections have become so popular that workers at Epicenter hold parties for those willing to get implanted.
“The biggest benefit I think is convenience,” said Patrick Mesterton, co-founder and CEO of Epicenter. As a demonstration, he unlocks a door by merely waving near it. “It basically replaces a lot of things you have, other communication devices, whether it be credit cards or keys.”
The technology in itself is not new. Such chips are used as virtual collar plates for pets. Companies use them to track deliveries. It’s just never been used to tag employees on a broad scale before. Epicenter and a handful of other companies are the first to make chip implants broadly available.
And as with most new technologies, it raises security and privacy issues. While biologically safe, the data generated by the chips can show how often an employee comes to work or what they buy. Unlike company swipe cards or smartphones, which can generate the same data, a person cannot easily separate themselves from the chip.
“Of course, putting things into your body is quite a big step to do and it was even for me at first,” said Mesterton, remembering how he initially had had doubts.
“But then on the other hand, I mean, people have been implanting things into their body, like pacemakers and stuff to control your heart,” he said. “That’s a way, way more serious thing than having a small chip that can actually communicate with devices.”
Epicenter, which is home to more than 100 companies and some 2,000 workers, began implanting workers in January 2015. Now, about 150 workers have them. A company based in Belgium also offers its employees such implants, and there are isolated cases around the world where tech enthusiasts have tried this out in recent years.
The small implants use Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, the same as in contactless credit cards or mobile payments. When activated by a reader a few centimeters (inches) away, a small amount of data flows between the two devices via electromagnetic waves. The implants are “passive,” meaning they contain information that other devices can read, but cannot read information themselves.
“The biggest benefit I think is convenience,” said Patrick Mesterton, co-founder and CEO of Epicenter. As a demonstration, he unlocks a door by merely waving near it. “It basically replaces a lot of things you have, other communication devices, whether it be credit cards or keys.”
The technology in itself is not new. Such chips are used as virtual collar plates for pets. Companies use them to track deliveries. It’s just never been used to tag employees on a broad scale before. Epicenter and a handful of other companies are the first to make chip implants broadly available.
And as with most new technologies, it raises security and privacy issues. While biologically safe, the data generated by the chips can show how often an employee comes to work or what they buy. Unlike company swipe cards or smartphones, which can generate the same data, a person cannot easily separate themselves from the chip.
“Of course, putting things into your body is quite a big step to do and it was even for me at first,” said Mesterton, remembering how he initially had had doubts.
“But then on the other hand, I mean, people have been implanting things into their body, like pacemakers and stuff to control your heart,” he said. “That’s a way, way more serious thing than having a small chip that can actually communicate with devices.”
Epicenter, which is home to more than 100 companies and some 2,000 workers, began implanting workers in January 2015. Now, about 150 workers have them. A company based in Belgium also offers its employees such implants, and there are isolated cases around the world where tech enthusiasts have tried this out in recent years.
The small implants use Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, the same as in contactless credit cards or mobile payments. When activated by a reader a few centimeters (inches) away, a small amount of data flows between the two devices via electromagnetic waves. The implants are “passive,” meaning they contain information that other devices can read, but cannot read information themselves.
If you enjoy the TradCatKnight blogs, please recommend above as a contributor!
Read more and watch related video at article link above.

The contributor has disabled comments for this story