| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
Dark Matter May Be Smoother than Expected
Analysis of a giant new galaxy survey, made with ESO’s VLT Survey Telescope in Chile, suggests that dark matter may be less dense and more smoothly distributed throughout space than previously thought. An international team used data from the Kilo Degree Survey (KiDS) to study how the light from about 15 million distant galaxies was affected by the gravitational influence of matter on the largest scales in the Universe. The results appear to be in disagreement with earlier results from the Planck satellite.
By exploiting the exquisite image quality available to the VST at the Paranal site, and using innovative computer software, the team were able to carry out one of the most precise measurements ever made of an effect known as cosmic shear. This is a subtle variant of weak gravitational lensing, in which the light emitted from distant galaxies is slightly warped by the gravitational effect of large amounts of matter, such as galaxy clusters.
In cosmic shear, it is not galaxy clusters but large-scale structures in the Universe that warp the light, which produces an even smaller effect. Very wide and deep surveys, such as KiDS, are needed to ensure that the very weak cosmic shear signal is strong enough to be measured and can be used by astronomers to map the distribution of gravitating matter. This study takes in the largest total area of the sky to ever be mapped with this technique so far.
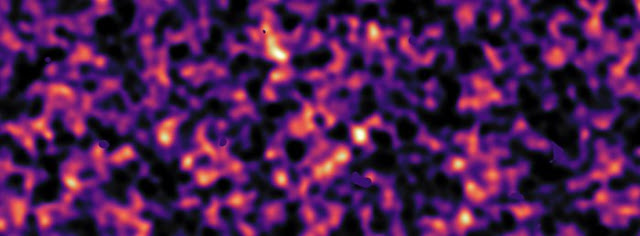
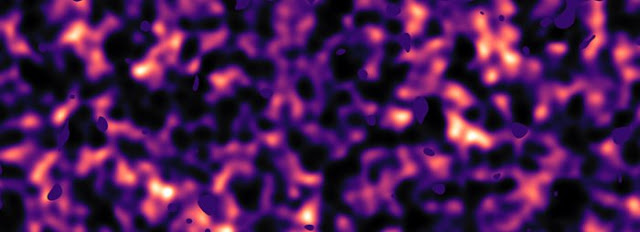
This video shows the location of one of the five KiDS regions that were surveyed by the VLT Survey Telescope at ESO’s Paranal Observatory in Chile. This region (known as G12) covers a large area of sky along the celestial equator in the constellations of Leo (The Lion) and Virgo (The Virgin). The final colour dark matter density image reveals an expansive web of dense (light) and empty (dark) regions. This image reconstruction was made by analysing the light collected from over three million distant galaxies more than 6 billion light-years away.
Credit: Kilo-Degree Survey Collaboration/H. Hildebrandt & B. Giblin/ESO/N. Risinger (skysurvey.org). Music: Konstantino Polizois (soundcloud.com/konstantino-polizois).
Massimo Viola explains: “This latest result indicates that dark matter in the cosmic web, which accounts for about one-quarter of the content of the Universe, is less clumpy than we previously believed.”
Dark matter remains elusive to detection, its presence only inferred from its gravitational effects. Studies like these are the best current way to determine the shape, scale and distribution of this invisible material.
The surprise result of this study also has implications for our wider understanding of the Universe, and how it has evolved during its almost 14-billion-year history. Such an apparent disagreement with previously established results from Planck means that astronomers may now have to reformulate their understanding of some fundamental aspects of the development of the Universe.
Hendrik Hildebrandt comments: “Our findings will help to refine our theoretical models of how the Universe has grown from its inception up to the present day.”
:
The KiDS analysis of data from the VST is an important step but future telescopes are expected to take even wider and deeper surveys of the sky.
The co-leader of the study, Catherine Heymans of the University of Edinburgh in the UK adds: “Unravelling what has happened since the Big Bang is a complex challenge, but by continuing to study the distant skies, we can build a picture of how our modern Universe has evolved.”
“We see an intriguing discrepancy with Planck cosmology at the moment. Future missions such as the Euclid satellite and the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope will allow us to repeat these measurements and better understand what the Universe is really telling us,” concludes Konrad Kuijken (Leiden Observatory, the Netherlands), who is principal investigator of the KiDS survey.
Notes
[1] The international KiDS team of researchers includes scientists from Germany, the Netherlands, the UK, Australia, Italy, Malta and Canada.
[2] This corresponds to about 450 square degrees, or a little more than 1% of the entire sky.
[3] The parameter measured is called S8. Its value is a combination of the size of density fluctuations in, and the average density of, a section of the Universe. Large fluctuations in lower density parts of the Universe have an effect similar to that of smaller amplitude fluctuations in denser regions and the two cannot be distinguished by observations of weak lensing. The 8 refers to a cell size of 8 megaparsecs, which is used by convention in such studies.
More information
Contacts and sources:
This research was presented in the paper entitled “KiDS-450: Cosmological parameter constraints from tomographic weak gravitational lensing”, by H. Hildebrandt et al., to appear in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Source: