| Online: | |
| Visits: | |
| Stories: |
Ancient Egyptian History Timeline
Egypt’s population was about 1 million by the time King Narmer united the “two lands” in 3100 B.C.E. The 375 years of the Early Dynastic Period (3000 B.C.E.–2625 B.C.E.) saw the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under strong central rule. During Dynasties 0 to 3 the capital city of Memphis was founded, and Egypt’s huge, bureaucratic government rapidly developed.
They are portrayed speaking directly to the gods and thinking lofty thoughts. They did not hesitate to pour all Egypt’s resources into building lavish tombs for themselves. By the end of the Old Kingdom, Egypt’s population had grown to 2 million, mostly extremely poor peasants.
There was general unhappiness with increasingly expensive royal building projects. Powerful, wealthy local rulers started ignoring the king, and splintered Egypt into inde- pendent feudal provinces. Climate changes brought a disastrous series of low Niles, causing crop failures, widespread famine, and the miseries of the First Intermediate Period (2130 B.C.E.–1980 B.C.E.). For 150 years, Egypt suffered chaos, civil war, and famine.
They did not want a repeat. For 350 years, Egypt enjoyed peace, prosperity, increased trade, and great practical achievements. The population grew to about 2.5 million. For the first time, Egypt had a middle class.
The Second Intermediate Period (1630 B.C.E.–1539 B.C.E.) brought Egypt’s worst nightmare: rule by foreigners. Another period of climate change and unstable Nile years brought crop failure, famine, and civil disorder. The Hyksos (“rulers of foreign lands”), foreigners of Semitic origin, took advantage and seized the throne, holding it for more than 100 years.
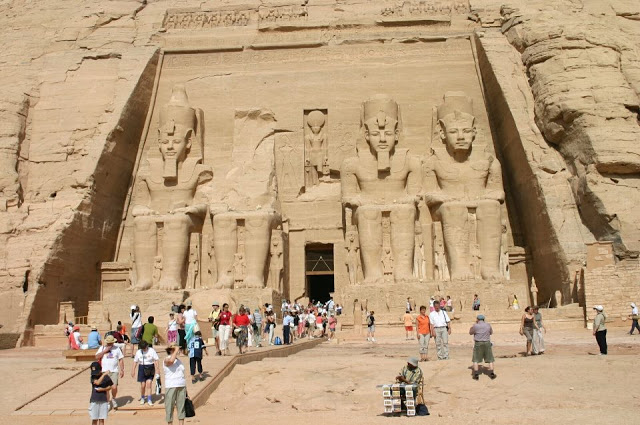
The New Kingdom (1539 B.C.E.–1075 B.C.E.) was Egypt’s imperial age. At its greatest extent, Egypt’s empire stretched from the fourth cataract of the Nile deep in Nubia all the way to the Euphrates River in Asia. Egypt was powerful and wealthy beyond compare—the world’s first superpower. The imperial pharaohs of the New Kingdom have proud, confident faces.
They owned the world. They thought extreme- ly highly of Egypt, and even more highly of themselves. No boast was too grand, no monument too large, no conquest too challenging for these mighty pharaohs. For more than 450 years, Egypt, now home to about 3 million people, was on top of the world. Gold, gifts, plunder, and tribute flowed in like the Nile floods.
But winds of change were blowing. During the 419 years of the Third Intermediate Period (1075 B.C.E.–664 B.C.E.) Egypt’s power weakened and, eventually, the empire came to an end. By around 1000 B.C.E., Egypt was just about bankrupt.
The country splintered into numerous small kingdoms and fiefdoms, constantly at war. Massive confusion reigned, enabling Egypt’s former colony, Nubia, to seize the throne, which it held for more than 100 years. During Egypt’s Late Period (664 B.C.E.–332 B.C.E.) outside influ- ences and invaders Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, and Macedonian Greeks dominated Egypt. A dynasty of merchant-kings, the Saites, fell to the Persian Cambyses in 525 B.C.E.
The First Persian Occupation (525 B.C.E.–405 B.C.E.) was an unhappy time. Egypt did not like being part of someone else’s empire. The Egyptians rebelled and won back their inde- pendence for 66 years. Nakhthoreb (also known as Nectanebo II), the last king of the Thirtieth Dynasty, who ruled from 362 B.C.E. to 343 B.C.E., was the last native Egyptian to rule Egypt for 2,300 years, until 1952.
The Second Persian Occupation (343 B.C.E.–332 B.C.E.) was brief and troubled. Egypt longed for a savior. In 332 B.C.E., Alexander the Great drove the hated Persians from Egypt, beginning the Hellenistic (Greek) Pe- riod (332 B.C.E.–323 B.C.E.). The Egyptians considered Alexander a god— the son of their god Amun-Re. In founding the city of Alexandria, Alexander brought Egypt into the greater Mediterranean world. But Egypt’s ancient, native civilization was swiftly passing away.
The Ptolemaic Period (323 B.C.E.–30 B.C.E.) saw the end of ancient Egypt. The Ptolemies, ruling from Alexandria, were greatly influenced by the Greeks, and Greek and Egyptian culture began to blend. In 30 B.C.E., Queen Cleopatra VII committed suicide rather than face defeat by the Romans, and Egypt became a province of the Roman Empire.
what year did the egyptian empire start
start of ancient egypt
ancient egypt history summary
archaic egyptian
where did egyptian civilization began
egyptian civilization developed
beginning of egyptian history
beginning of egypt
ancient egyptian civilization time period
what year did the egyptian civilization began
history and culture of egypt
ancient egypt expansion
the fall of egyptian empire
egyptian history is divided into
the period of egyptian history known as the
world history ancient egypt
interactive ancient egypt websites
egyption period
ancient egyptian land
egyptian civilization period
what did ancient egyptians
ancient egyptian time period
egyptian age
time period ancient egypt
neolithic egypt
the ancient egypt site
ancient egypt beginning
kingdoms in egypt
where ancient egypt is located
ancient egypt information facts
what happened to ancient egyptian civilization
egyptian civilization for kids project
early ancient egypt
egyptian civilization sources
kingdoms of ancient egypt
where is the egyptian civilization located
civilisation of ancient egypt
the fall of egyptian civilization
the beginning of ancient egypt
egypt established
what was egypt
ancient egypt end
the egyptian period
the nile valley civilization of egypt
fall of egyptian empire
where is ancient egypt located today
time period for ancient egypt
ancient egyptian sources
ancient egyptian civilization information
what happened to egyptian civilization
early egyptian
old egyptian civilization
time period of egypt
end of the egyptian empire
ancient egypt development
what time period did ancient egypt exist
the land of ancient egypt
who conquered egypt
age of egypt
who were the ancient egyptian
where was ancient egypt
how did ancient egypt fall
end of ancient egypt
egypt period
egyptian civilization time period
egypt uprising
when did ancient egypt start
the ancient egyptian civilization is known for
when did ancient egypt end
the fall of the egyptian empire
how long did ancient egypt last
where is ancient egypt
what time was ancient egypt
what year was ancient egypt
prehistoric egypt
fall of egyptian civilization
egypt protests
first egyptians
where did the egyptian civilization began
egyptian time
egypt era
when was egypt founded
egyptian historian
where was egypt
when was ancient egypt
describe ancient egypt
when did ancient egypt begin
ancient egypt kingdoms
how old is egypt
how long did the egyptian empire last
ancient egyptian kingdoms
the fall of ancient egypt
beginning of ancient egypt
what did the ancient egyptians
old egypt
images of egyptian civilization
what was ancient egypt
ancient egyptian period
where was ancient egypt located
pyramids of egypt location
what year did ancient egypt start
time of ancient egypt
location ancient egypt
early egypt
asian egypt
greatest egypt
ancient egypt sources
where did the ancient egyptians come from
ancient egypt period
what time period did the egyptian civilization exist
egypt early civilization
history in egypt
egypt civilization facts
early civilization in egypt
all about the ancient egypt
egyptian civilization summary
beginning of egyptian civilization
location of egyptian civilization
history about ancient egypt
ancient egyptian culture summary
information of ancient egypt
Source: http://egy-king.blogspot.com/2017/03/ancient-egyptian-history-timeline.html