| Visitors Now: | |
| Total Visits: | |
| Total Stories: |

| Story Views | |
| Now: | |
| Last Hour: | |
| Last 24 Hours: | |
| Total: | |
Voyager 1 Detecting Interstellar wind
From
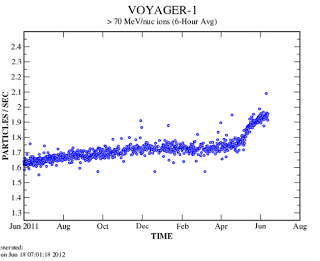
Voyager 1 is detecting an increase in cosmic rays. This could be indicating it is crossing over into interstellar space. This crossover could take some time.
In 2011, NASA was indicating that Voyager is close to the edge of the solar system.
Scientists analyzing recent data from NASA's Voyager and Cassini spacecraft have calculated that Voyager 1 could cross over into the frontier of interstellar space at any time and much earlier than previously thought. The findings are detailed in this week's issue of the journal Nature.
The Voyager-1 spacecraft was launched on September 5, 1977 and subsequently encountered Jupiter on March 5, 1979 and Saturn on November 12, 1980.
The Voyager-2 spacecraft was launched on August 20, 1977 and subsequently encountered Jupiter on July 9, 1979; Saturn on August 25, 1981; Uranus on January 24, 1986, and Neptune on August 25, 1989.
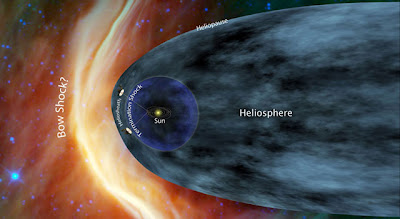
Both space craft are now traveling out of the Solar System in the "termination shock" phase of their interstellar mission. The trajectory of Voyager-1 is taking it toward the nose of the Sun's heliosphere above the ecliptic while the trajectory of Voyager-2 is taking it toward the nose of the Sun's heliosphere below the ecliptic.
Voyager 1 crossed the termination shock on December 16, 2004, and Voyager 2 crossed on August 30, 2007, on their way to the heliopause and interstellar space.
Nature – Zero outward flow velocity for plasma in a heliosheath transition layer
See more and subscribe to NextBigFuture at
Source: